-
+86 15030157877
-
sales@galvanizedmetalmesh.com
dec . 04, 2024 18:20 Back to list
perforated metal factory
The Perforated Metal Factory Manufacturing Precision and Versatility
In the world of modern manufacturing, perforated metal has emerged as a vital material that embodies both functionality and aesthetic appeal. At the heart of this industry lies the perforated metal factory, a hub of innovation and craftsmanship where solid sheets of metal are transformed into versatile products that serve diverse applications. This article explores the intricacies of a perforated metal factory, the manufacturing process, and the myriad uses of perforated metal in various sectors.
Understanding Perforated Metal
Perforated metal is created by punching holes into a sheet of metal, resulting in a pattern of openings that can vary in size, shape, and distribution. This unique manufacturing technique provides several advantages, including weight reduction, ventilation, acoustic properties, and decorative appeal. From industrial applications to architectural designs, perforated metal is increasingly recognized as a multifaceted material that balances both utility and visual impact.
The Manufacturing Process
The production of perforated metal begins with selecting the appropriate metal substrate, which can range from aluminum and stainless steel to copper and brass. Each type of metal offers distinct properties, making it suitable for different applications. For instance, stainless steel is favored in environments requiring corrosion resistance, while aluminum is prized for its lightweight characteristics.
Once the metal sheet is chosen, the perforation process begins. Modern perforated metal factories employ advanced machinery that utilizes CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology, ensuring precision in hole placement and size. The punching process can produce a continuous sheet of perforated metal or custom sections based on client specifications. Options for hole patterns are virtually limitless, accommodating anything from simple round holes to intricate designs and layouts.
After the perforation phase, additional finishing processes may be applied, such as deburring, surface treatment, or coating to enhance durability and aesthetics. These finishes not only protect the metal from oxidation and wear but also add a layer of visual appeal, making perforated panels suitable for both functional and decorative applications.
perforated metal factory
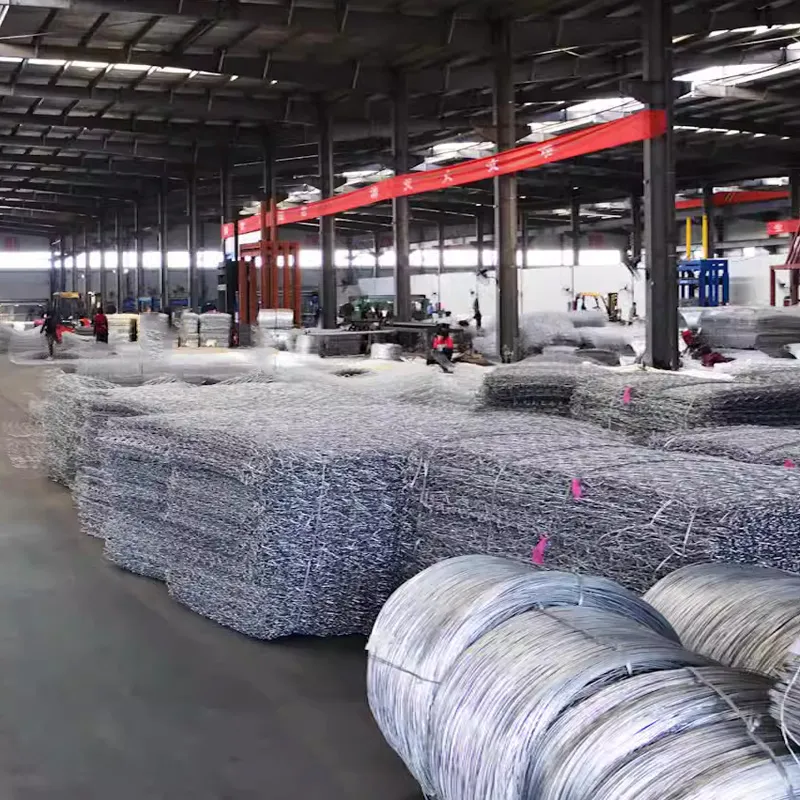

Applications of Perforated Metal
The versatility of perforated metal makes it suitable for numerous applications across various industries. In the architectural realm, perforated metal panels are widely used for facades, sunshades, and room dividers. They allow for natural light penetration while providing privacy and reducing heat gain in buildings. Many contemporary designs incorporate perforated metal as an element of style, seamlessly blending engineering with art.
In the automotive and aerospace industries, perforated metal components serve crucial roles in weight reduction and airflow management. Grilles, heat shields, and filtration systems are just a few examples of how perforated materials contribute to overall performance and efficiency.
The industrial sector also greatly benefits from perforated metal. It is commonly used in manufacturing equipment, safety guards, and scaffolding, providing strength without unnecessary weight. Moreover, the electrical industry utilizes perforated sheets for transformer covers and switchgear cabinets, ensuring adequate ventilation while protecting sensitive components.
Sustainability and Innovation
As industries move towards more sustainable practices, perforated metal factories are also adapting to meet eco-friendly standards. Recyclability of metals and energy-efficient manufacturing processes contribute to reducing the carbon footprint of productions. Innovations in design and technology, such as the introduction of laser-cutting techniques, further enhance the capabilities and precision of perforated metal production.
In conclusion, perforated metal factories represent a remarkable blend of tradition and modernity in manufacturing. By leveraging advanced technologies and sustainable practices, these factories produce materials that are not only functional but also aesthetically pleasing. The diverse applications of perforated metal, spanning architecture, automotive, industrial sectors, and beyond, underscore its significance in shaping the future of manufacturing. As demand for customized and efficient solutions continues to grow, the role of perforated metal will undoubtedly become even more integral to innovation and design.
-
Premium Security Window Screen Mesh | Unmatched Safety
NewsAug.05,2025
-
Premium Artificial Grass Fence | AI Design Privacy Solution
NewsAug.04,2025
-
Premium Hexagonal Gabion Mesh Solutions | Durable & Eco-Friendly
NewsAug.03,2025
-
Smart AI Fence Solutions with GPT-4 Turbo | Secure & Fast
NewsAug.02,2025
-
Welded Gabion Solutions: Durable & AI-Enhanced Designs
NewsAug.01,2025
-
Premium Welded Gabion Mesh | Robust & Eco-Friendly
NewsJul.31,2025