-
+86 15030157877
-
sales@galvanizedmetalmesh.com
Авг . 13, 2024 09:22 Back to list
Exploring the Innovative Manufacturing Processes in the Wire Netting Industry and Their Economic Impact
The Evolution and Importance of Wire Netting Factories
Wire netting has become an indispensable part of various industries due to its versatility and structural integrity. The establishments that manufacture these products—wire netting factories—play a significant role in the construction, agriculture, and packaging sectors, providing essential materials that support a myriad of applications. Understanding the evolution and importance of these factories can shed light on their critical position in today’s economy.
Wire netting, often referred to as welded wire mesh or wire netting, consists of metal wires intersected and held together in a grid pattern. This design provides strength while maintaining a lightweight profile, making it suitable for fencing, reinforcement in concrete, and even as supporting structures for crops in agricultural settings. The evolution of wire netting factories has been closely tied to advancements in technology and materials science.
Historically, wire netting production began with rudimentary handmade methods, utilized primarily for fencing and basic structural purposes. As industrialization progressed in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, factories began to emerge that employed mechanized processes to produce wire mesh more efficiently. This marked a significant shift; manufacturers could now meet the growing demand across various sectors, including agriculture, construction, and mining. The introduction of automated machinery has further revolutionized these factories, allowing for higher production rates and improved precision in the mesh patterns.
wire netting factories
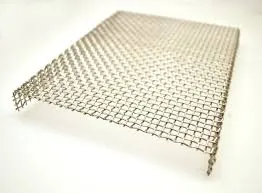
Currently, wire netting factories leverage advanced technologies such as computerized weaving and cutting machines, which enable them to produce a wide range of products tailored to specific needs. By utilizing materials such as galvanized steel, stainless steel, and PVC-coated wires, these factories can create durable and corrosion-resistant wire netting solutions. This versatility caters to various applications, from garden fencing and animal enclosures to reinforcement in construction projects and erosion control measures.
The significance of wire netting factories extends beyond their production capabilities. They contribute significantly to job creation in many regions, often serving as local economic hubs. By providing employment opportunities, these factories support the livelihoods of many families and contribute to the overall economic health of their communities. Additionally, they foster innovation by collaborating with research institutions to develop new products and improve existing ones, thus ensuring that they remain competitive in a global market.
In terms of environmental impact, many wire netting factories are increasingly adopting sustainable practices. They are focused on minimizing waste during production and enhancing the recyclability of their products. Some manufacturers are even exploring the use of eco-friendly materials, which appeals to a growing demographic of environmentally conscious consumers. By prioritizing sustainability, these factories not only mitigate their ecological footprint but also align themselves with global efforts towards responsible production practices.
In conclusion, wire netting factories are vital components of various sectors, shaping the landscape of construction, agriculture, and beyond. Their evolution from manual production to advanced manufacturing highlights the importance of technological advancements in this field. As they continue to innovate and adapt to changing market demands while fostering economic growth and sustainability, wire netting factories will undoubtedly remain a cornerstone of industry for years to come. Their enduring significance will shape the future of material production and its applications across a wide array of fields.
-
Welded Gabion Solutions: Durable & AI-Enhanced Designs
NewsAug.01,2025
-
Premium Welded Gabion Mesh | Robust & Eco-Friendly
NewsJul.31,2025
-
Premium Eco-Friendly Roof Tiles | Affordable & Durable
NewsJul.31,2025
-
Premium Roof Tiles for Durable & Stylish Roofing Solutions
NewsJul.30,2025
-
High-Quality Roof Tiles for Durable & Stylish Roofing Solutions
NewsJul.29,2025
-
High Quality Square Wire Mesh Manufacturer & Supplier for Wholesale
NewsJul.29,2025