-
+86 15030157877
-
sales@galvanizedmetalmesh.com
Jan . 06, 2025 18:48 Back to list
metal stainless steel perforated metal mesh
The evolution of architectural and industrial design frequently brings forth materials that balance functionality with aesthetic appeal. One such innovation is the metal mesh—a versatile solution employed across various sectors, from construction to interior design, and even in sophisticated engineering applications. This material stands as a testament to both human ingenuity and the ongoing quest for superior performance.
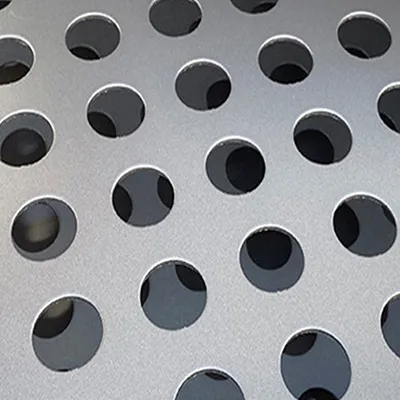
Metal meshes are crafted through intricate processes that involve weaving, welding, or perforating metals such as stainless steel, copper, or aluminum. These materials are chosen based on the specific requirements of the application, with factors such as durability, corrosion resistance, and malleability considered paramount. The meticulous process of creation ensures that metal mesh serves its purpose effectively whether it’s providing structural support or contributing to the visual aesthetics of a project.
In construction, metal mesh panels have become synonymous with modern architectural design. They offer an unmatched blend of strength and flexibility, creating facades that are both resilient and attractive. Their open-weave design allows for excellent ventilation, maintaining energy efficiency while providing essential protection against environmental elements. Furthermore, their capacity to diffuse natural light without compromising on privacy adds to their appeal. Architects continuously leverage these properties to craft innovative buildings that stand out in urban landscapes.
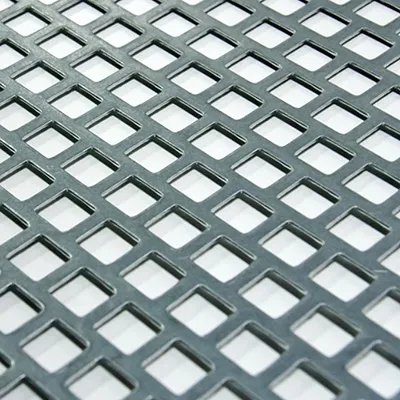
Interior designers, too, have embraced the versatility of metal mesh. When used in interior spaces, these meshes can transform mundane partitions into stunning focal points. The mesh can be powder-coated in various colors, adapting to any thematic requirement. Aside from aesthetic purposes, metal mesh is also employed in functional applications such as radiator covers, cabinet inserts, and stair railings, all of which benefit from the material’s robustness and visual appeal.
In industrial settings, metal mesh proves indispensable in engineering and manufacturing processes. It is used in filtration systems where its fine weaving can separate particles effectively in both air and liquid form. In automotive industries, mesh components are utilized in the design of radiator grilles and exhaust systems, showcasing their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and pressures while offering minimal resistance to airflow.
metal mesh
The trend toward sustainable design has also seen an uptick in the use of metal mesh. Being made of recyclable materials, metal meshes align with environmental goals, reducing waste and promoting sustainable architectural practices. Their long lifespan reduces the need for frequent replacements, further conserving resources.
Despite its advantages, selecting the right type of metal mesh requires expertise to ensure it meets the intended structural and aesthetic demands. Consulting with professionals in material science and engineering offers insight into optimal material choice, size of openings, and surface treatments to enhance performance. Such collaboration guarantees the implementation of solutions that are not only innovative but also reliable and durable.
Trust in metal mesh as a go-to solution is reinforced by stringent quality control standards adhered to by manufacturers. Certifications and regular inspections ensure products meet industry requirements, instilling confidence in those who specify or use these materials in their projects.
Metal mesh continues to prove itself as a product of exceptional prowess, balancing aesthetics, functionality, and sustainability. Whether for construction, interior design, or industrial applications, its adaptability and resilience make it an unparalleled choice. As industries advance, the potential uses for metal mesh seem boundless, promising ongoing innovation in both design and application. This material, with its combination of elegance and strength, provides a blueprint for future developments across a myriad of fields.
-
Premium Welded Gabion Mesh | Robust & Eco-Friendly
NewsJul.31,2025
-
Premium Eco-Friendly Roof Tiles | Affordable & Durable
NewsJul.31,2025
-
Premium Roof Tiles for Durable & Stylish Roofing Solutions
NewsJul.30,2025
-
High-Quality Roof Tiles for Durable & Stylish Roofing Solutions
NewsJul.29,2025
-
High Quality Square Wire Mesh Manufacturer & Supplier for Wholesale
NewsJul.29,2025
-
Premium Roof Tiles for Durable & Stylish Roofing Solutions
NewsJul.29,2025